"Glass frog" is a term given to a group of South and Central American arboreal frogs distinguished by a uniquely translucent skin, with some having a practically transparent underside of the abdomen which allows a clear view of working internal organs. A newly discovered species of glass frog, Hyalinobatrachium yaku, has been identified in Ecuador, according to an article recently published in the journal ZooKeys. One of the special features of this newly discovered variant is an almost completely see-through belly, where the heart, stomach, and blood vessels are on vivid display, albeit covered in some kind of white coating.
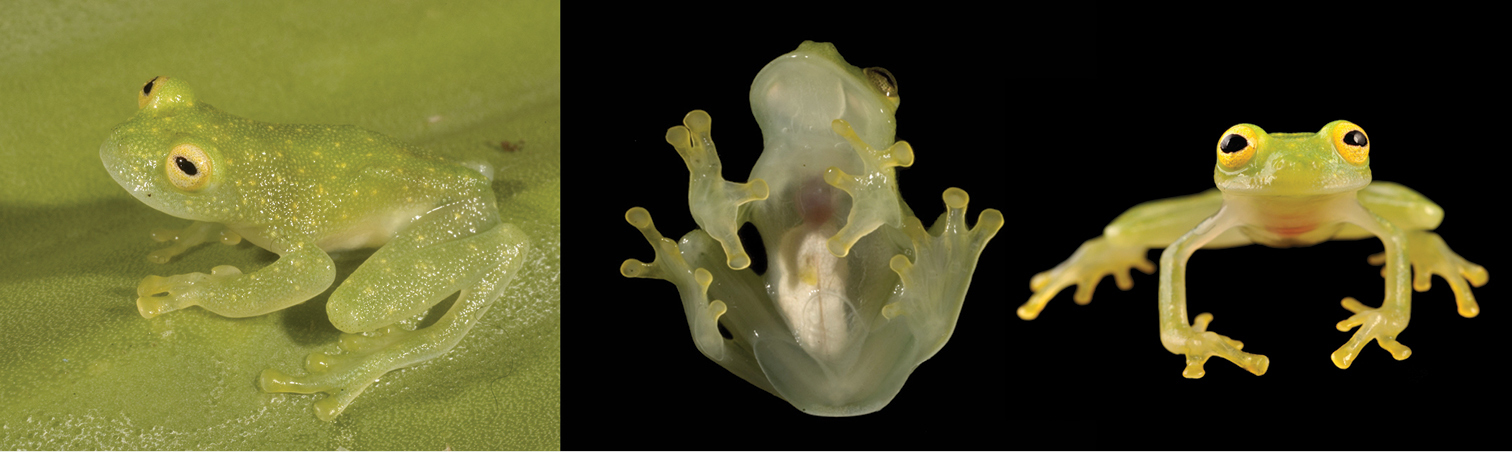 The same study announcing the new species discoveries points out the threats facing the newly identified glass frogs. Specifically, the authors point to the Ecuadorian government's plans to ramp up oil extraction in the area where the frogs were discovered, which can lead to threats such as water pollution and new road networks through the forests of the Amazonian lowlands that are the frog's natural habitat.
The same study announcing the new species discoveries points out the threats facing the newly identified glass frogs. Specifically, the authors point to the Ecuadorian government's plans to ramp up oil extraction in the area where the frogs were discovered, which can lead to threats such as water pollution and new road networks through the forests of the Amazonian lowlands that are the frog's natural habitat.
See the article for additional information about the newly discovered and fascinating glass frogs.